Servlets have become a popular and widely supported mechanism for providing dynamic content on the Internet. While servlets are defined in the [4] Java Servlet 3.1 Specification, the OSGi Http Whiteboard Specification provides a light and convenient way of using servlets, servlet filters, servlet listeners and web resources in an OSGi environment through the use of the [7] Whiteboard Pattern.
The Http Whiteboard specification supports:
-
Registering Servlets - Registering a servlet in the Service Registry makes it available to be bound to an endpoint to serve content over the network.
-
Registering Servlet Filters - Servlet filters support pre- and post-processing of servlet requests and responses. Servlet filters can be registered in the Service Registry to include them in the handling pipeline.
-
Registering Resources - Resources such as HTML files, JavaScript, image files, and other static resources can be made available over the network by registering resource services.
-
Registering Servlet Listeners - The servlet specification defines a variety of listeners, which receive callbacks when certain events take place.
Implementations of this specification can support the following versions of the HTTP protocol:
Alternatively, implementations of this service can support other protocols if these protocols can conform to the semantics of the Java Servlet API.
Http Whiteboard implementations must support version 3.1 or later of the Java Servlet API.
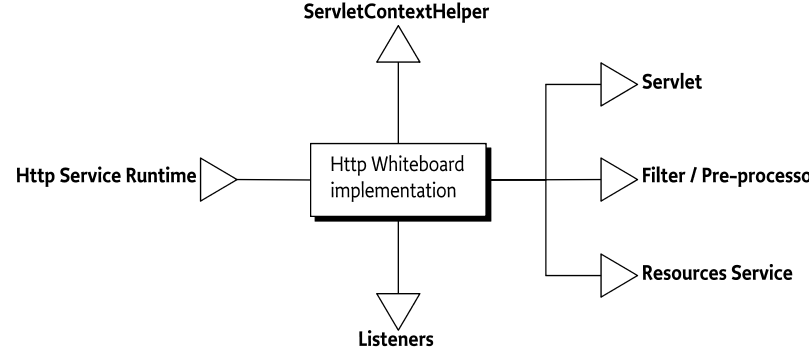
This specification defines the following entities:
-
Http Whiteboard service - An object registered in the Service Registry under one of the Whiteboard service interfaces defined by this specification.
-
Http Whiteboard implementation - An implementation that processes Http Whiteboard services.
-
Http Service Runtime service - Service providing runtime introspection into the Http Whiteboard implementation.
-
Listener - Various listeners can be registered to receive notifications about servlet or Http Session events.
-
Resource Service - A service thats binds static resources.
-
Servlet - Component that dynamically generates web pages or other resources provided over the network.
-
Servlet Context Helper - A service to control the behavior of the Servlet Context.
-
Servlet Filter - Can be used to augment or transform web resources or for cross-cutting functionality such as security, common widgets or otherwise.
The servlet specification defines the ServletContext
which is provided to servlets at runtime by the container. Whiteboard
services defined by this specification are also provided with a
ServletContext. The behavior of this Servlet Context can be
influenced by providing a ServletContextHelper service. A custom
ServletContextHelper can provide resources, mime-types,
handle security and supports a number of methods from the
ServletContext.
The Http Whiteboard implementation must create a separate
ServletContext instance for each
ServletContextHelper service. Whiteboard services can be
associated with the Servlet Context Helper by using the
osgi.http.whiteboard.context.select property. If this
property is not set, the default Servlet Context
Helper is used.
To achieve the required behavior for
ServletContext.getClassLoader each bundle must be provided
with a separate Servlet Context instance to serve the class loader of the
Whiteboard services for that bundle. For more information see
getClassLoader in Table 140.2 on page .
Some implementations of the ServletContextHelper may be
implemented using a Service Factory, for example to provide resources from
the associated bundle, as the default implementation
does. Therefore the Whiteboard implementation must get the Servlet Context
Helper using the Bundle Context of the bundle that registered the
Whiteboard service.
Some environments may use [8] Core Service Hooks to isolate
ServletContextHelper service registrations. For example,
Subsystem Service Specification. The Whiteboard implementation must
check that the bundle registering the Whiteboard service has the ability
to find the ServletContextHelper service before allowing the
Whiteboard service to bind to the Servlet Context Helper. This can be done
by calling one of the getServiceReferences methods on the
Bundle Context of bundle that registered the Whiteboard service.
Table 140.1 Service registration properties for
ServletContextHelper services.
| Service Property | Type | Description |
|---|---|---|
|
|
required |
Name of the Servlet Context Helper. This name can be
referred to by Whiteboard services via the
Registrations with an invalid or unspecified name are not used and reflected in the failure DTOs. See HTTP_WHITEBOARD_CONTEXT_NAME. |
|
|
required |
Additional prefix to the context path for servlets.
This property is mandatory. Valid characters are specified in IETF
RFC 3986, section 3.3. The context path of the default Servlet
Context Helper is |
context.init.* |
optional |
Properties starting with this prefix are provided as
init parameters through the
|
Multiple ServletContextHelper services can have
identical or overlapping osgi.http.whiteboard.context.path
values. A matching servlet or resource is located as follows:
-
The Servlet Context Helper service with the longest matching path is matched first.
-
In the case of two Servlet Context Helpers with the same path, the service with the highest ranking is searched first for a match. In the case of a tie, the lowest service ID is searched first.
For example, if two ServletContextHelper services are
registered as follows
osgi.http.whiteboard.context.path = /foo
osgi.http.whiteboard.context.path = /foo/bar Then a request
for http://localhost/foo/bar/someServlet is looked up in the
following order:
-
/foo/barcontext looking for a pattern to match/someServlet -
/foocontext looking for a pattern to match/bar/someServlet
Note that whole path segments must match. Therefore the
following request can only be handled by the Servlet Context Helper
registered under the /foo path:
http://localhost/foo/bars/someOtherServlet.
For details on the association process between servlet, servlet
filter, resource and listener services and the
ServletContextHelper see Common Whiteboard Properties.
If a Servlet Context Helper can not be used, for example because it
is shadowed by another Servlet Context Helper service with the same name,
but with a higher ranking, this is reflected in the FailedServletContextDTO. Similarly, if an alternative default
Servlet Context Helper is provided, the default Servlet Context Helper
provided by the Http Whiteboard implementation is not used and represented
in a failure DTO.
An example Servlet Context Helper defined using Declarative Services
annotations can be found below, it prefixes the path with
/myapp for any associated whiteboard service. Additionally,
it serves static resources from a non-standard location, a content
delivery network. Other methods use the default
ServletContextHelper implementation.
@Component(service = ServletContextHelper.class, scope = ServiceScope.BUNDLE)
@HttpWhiteboardContext(name = "my-context", path = "/myapp")
public class CDNServletContextHelper extends ServletContextHelper {
public URL getResource(String name) {
try {
return new URL("http://acmecdn.com/myapp/" + name);
} catch (MalformedURLException e) {
return null;
}
}
}The following sections outline the methods a custom ServletContextHelper can override and the behavior of the default implementation.
Called to provide the MIME type for a resource.
Default Behavior - Always returns
null.
Called to support the ServletContext.getRealPath
method.
Default Behavior - Always returns
null.
Obtain a URL for a given resource request.
Default Behavior - Assumes the resources are
in the bundle registering the Whiteboard service. Its
Bundle.getEntry method is called to obtain a URL to the
resource. The default Servlet Context Helper implementation assumes the
path to be relative to the bundle's root.
Called to support the ServletContext.getResourcePaths
method. Returns all the matching resources for the path.
Default Behavior - Assumes the resources are
in the bundle registering the Whiteboard service. Its
Bundle.findEntries method is called to obtain the
listing.
The handleSecurity(javax.servlet.http.HttpServletRequest,javax.servlet.http.HttpServletResponse) method is invoked to handle implementation-defined security on the request. It is invoked before the request is sent to the filter-servlet pipeline.
When the request returns from the filter-servlet pipeline the
finishSecurity(javax.servlet.http.HttpServletRequest,javax.servlet.http.HttpServletResponse) method is called. This method can be used by the
security handling mechanism to clean up any context associated with the
current request. finishSecurity is only called if
handleSecurity returned true for the specified
request. If an exception occurs during processing of the pipeline,
finishSecurity is still called. This allows to clean up
regardless of the result of the pipeline.
In the case a request is dispatched either using the include or
forward method handleSecurity and
finishSecurity are called again on this new context. These
calls are nested within the originating request. Servlet Context Helpers
that implement these methods must be prepared to deal with such nested
invocations.
Default Behavior -
handleSecurity always returns true.
finishSecurity does nothing by default.
The ServletContext provided to Whiteboard services is
based on the associated ServletContextHelper, Whiteboard
service registration properties and the underlying servlet
container.
Methods to programmatically add servlets, servlet filters and
listeners are not supported on the ServletContext. Such
functionality is available by registering these entities as Whiteboard
services.
Table 140.2 Behavior of ServletContext methods.
| ServletContext method | Since | Description |
|---|---|---|
addFilter(...) |
3.0 |
Throws
|
addListener(...) |
3.0 |
Throws
|
addServlet(...) |
3.0 |
Throws
|
createFilter(Class) |
3.0 |
Throws
|
createListener(Class) |
3.0 |
Throws
|
createServlet(Class) |
3.0 |
Throws
|
declareRoles(String ...) |
3.0 |
Throws
|
getAttribute(String) |
2.0 |
Stored per |
getAttributeNames() |
2.1 |
Stored per |
getClassLoader() |
3.0 |
Returns the class loader of the bundle that registered the Whiteboard service. An implementation of this specification can achieve this by returning separate façades of the ServletContext to each Whiteboard service. Each façade accesses the Whiteboard service's Bundle Wiring to obtain its class loader. |
getContext(String) |
2.1 |
Backed by the Servlet Container. |
getContextPath() |
2.5 |
Return the web context path of the Servlet Context.
This takes into account the
|
getDefaultSessionTrackingModes() |
3.0 |
Backed by the Servlet Container. |
getEffectiveMajorVersion() |
3.0 |
Backed by the Servlet Container. |
getEffectiveMinorVersion() |
3.0 |
Backed by the Servlet Container. |
getEffectiveSessionTrackingModes() |
3.0 |
Backed by the Servlet Container. |
getFilterRegistration(String) |
3.0 |
Backed by the Servlet Container. |
getFilterRegistrations() |
3.0 |
Backed by the Servlet Container. |
getInitParameter(String) |
2.2 |
From |
getInitParameterNames() |
2.2 |
From |
getJspConfigDescriptor() |
3.0 |
Returns |
getMajorVersion() |
2.1 |
Backed by the Servlet Container. |
getMimeType(String) |
2.1 |
Backed by the
|
getMinorVersion() |
2.1 |
Backed by the Servlet Container. |
getNamedDispatcher(String) |
2.2 |
Provides the Whiteboard servlet with the specified
name, provided through the
|
getRealPath(String) |
2.0 |
Backed by the
|
getResource(String) |
2.1 |
Backed by the
|
getRequestDispatcher(String) |
2.1 |
If the argument matches a servlet associated with this Servlet Context Helper, this will be returned. |
getResourceAsStream(String) |
2.1 |
Backed by the
|
getResourcePaths(String) |
2.3 |
Backed by the
|
getServlet(String) |
2.0 |
Deprecated. Backed by the Servlet Container. |
getServletContextName() |
2.2 |
The name of the |
getServletNames() |
2.0 |
Deprecated. Backed by the Servlet Container. |
getServletRegistration(String) |
3.0 |
Backed by the Servlet Container. |
getServletRegistrations() |
3.0 |
Backed by the Servlet Container. |
getServlets() |
2.0 |
Deprecated. Backed by the Servlet Container. |
getServerInfo() |
2.0 |
Backed by the Servlet Container. |
getSessionCookieConfig() |
3.0 |
Returns a |
getVirtualServerName() |
3.1 |
Backed by the Servlet Container. |
log(String) |
2.0 |
Backed by the Servlet Container. |
log(Exception, String) |
2.0 |
Deprecated. Backed by the Servlet Container. |
log(String, Throwable) |
2.1 |
Backed by the Servlet Container. |
removeAttribute(String) |
2.1 |
Stored per |
setAttribute(String, Object) |
2.1 |
Stored per |
setInitParameter(String, String) |
3.0 |
Throws |
setSessionTrackingModes(Set) |
3.0 |
Throws |
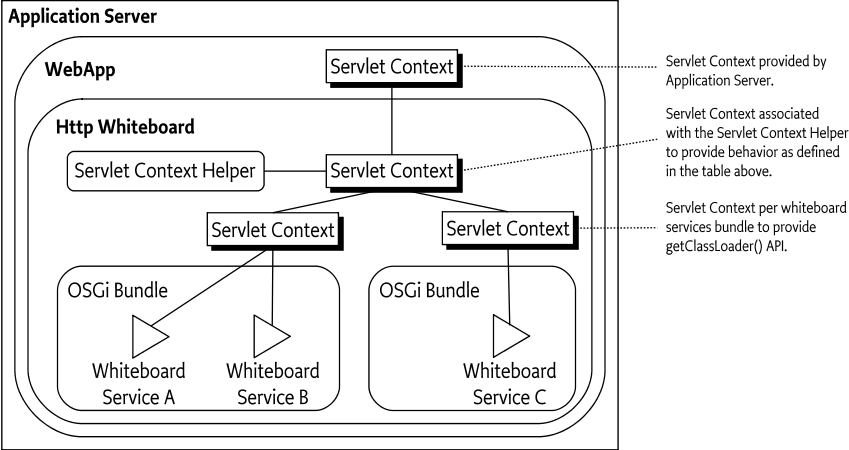
Implementations of this specification will often be backed by existing servlet containers or a Java EE application server. There may also exist implementations which bridge into a servlet container into which the OSGi Framework has been deployed as a Web Application.
In bridged situations the Http Whiteboard implementation will live
in one servlet context and all Whiteboard services registered by this
implementation will be backed by the same underlying Servlet Context.
However, to exhibit the behavior described in Table 140.2 on page different Servlet Context
objects may be required. Therefore an implementation of this
specification may need to create additional ServletContext
objects which delegate certain functionality to the
ServletContextHelper and other functionality to the Servlet
Context of the Web Application, yet further functionality can be
obtained otherwise. In such cases the relationship may look like the
below figure.
Where Table 140.2 on page states Backed by the Servlet Container and the Http Whiteboard implementation is deployed in bridged mode, the API call can be forwarded to the top-level Servlet Context. If the Http Whiteboard implementation is not deployed in bridged mode, it must provide another means to handle these APIs.
In bridged deployments, the implementation needs to ensure the following:
-
That Whiteboard services are provided with the correct
ServletContextkeeping in mind that each distinctServletContextHelpershould be associated with a separateServletContextobject, which in turn may delegate certain requests to the underlying sharedServletContextas described in the table above. -
That Http Sessions are not shared amongst servlets registered with different
ServletContextHelpers. That is,HttpRequest.getSessioncalls must provide different sessions per associatedServletContextHelper. Http Sessions are defined in chapter 7 of the [4] Java Servlet 3.1 Specification.
Whiteboard servlet, servlet filter, resource and listener services
support common service registration properties to associate them with a
ServletContextHelper and/or a Http Whiteboard
implementation.
Table 140.3 Common properties
| Service Property | Type | Description |
|---|---|---|
|
|
optional |
An LDAP-style filter to select the associated ServletContextHelper service to use. Any service property of the Servlet Context Helper can be filtered on. If this property is missing the default Servlet Context Helper is used. For example, to select a Servlet Context Helper
with name To select all Servlet Context Helpers provide the following value: If no matching context exists this is reflected in the failure DTOs. See HTTP_WHITEBOARD_CONTEXT_SELECT. |
|
|
optional |
The value of this service property is an LDAP-style
filter expression to select the Http Whiteboard implementation(s)
to handle this Whiteboard service. The LDAP filter is used to
match HttpServiceRuntime services. Each Http Whiteboard
implementation exposes exactly one
|
If multiple Servlet Context Helper services match the
osgi.http.whiteboard.context.select property the servlet,
filter, resource or listener will be registered with all these Servlet
Context Helpers. To avoid multiple init and
destroy calls on the same instance, servlets and filters
should be registered as Prototype Service Factory.
Servlets can be registered with the Http Whiteboard implementation
by registering them as Whiteboard services. This means that
Servlet implementations are registered in the Service
Registry under the javax.servlet.Servlet interface.
Servlets are registered with one or more pattern through the
osgi.http.whiteboard.servlet.pattern service property. Each
pattern defines the URL context that will trigger the servlet to handle
the request. They are defined by the [4] Java Servlet 3.1 Specification in section 12.2,
Specification of Mappings. Note that these mapping
rules are slightly different than those defined in the Http Service Specification. The mapping rules are:
-
A string beginning with a '/' character and ending with a "/*" suffix is used for path mapping.
-
A string beginning with a "*." prefix is used as an extension mapping.
-
The empty string ("") is a special URL pattern that exactly maps to the application's context root. That is, requests of the form http://host:port/<context-root>/. In this case the path info is "/" and the servlet path and context path are the empty string ("").
-
A string containing only the '/' character indicates the "default" servlet of the application. In this case, the servlet path is the request URI minus the context path and the path info is null.
-
All other strings are used for exact matches only.
Servlet and resource service registrations associated
with a single Servlet Context share the same namespace. In case of
identical registration patterns, service ranking rules are used to select
the service handling a request. That is, Whiteboard servlets that have
patterns shadowed by other Whiteboard services associated with the
same Servlet Context are represented in the failure
DTOs.
The above rules can cause servlets that are already bound becoming unbound if a better match arrives. This ensures a predictable end result regardless of the order in which services are registered.
A servlet may be registered with the property
osgi.http.whiteboard.servlet.name which can be used by
servlet filters to address this servlet. If the servlet service does not
have this property, the servlet name defaults to the fully qualified class
name of the service object.
With implementations that both implement this specification as well as the Http Service Specification, situations can arise where a servlet is registered for the same pattern with the Http Service as well as with the Http Whiteboard. The Servlet Context of the Http Service is treated in the same way as all contexts managed by the Whiteboard implementation. The highest ranking is associated with the context of the Http Service. For a request, contexts are processed in the order as described in section The Servlet Context.
For example, if the Http Whiteboard implementation is listening on
port 80 on the machine www.acme.com and the
Servlet object is registered with the pattern
"/servlet", then the Servlet object's
service method is called when the following URL is used from
a web browser:
http://www.acme.com/servletThe following table describes the properties that can be used by
Servlets registered as Whiteboard services. Additionally, the
common properties listed in Table 140.3 on page are supported.
Table 140.4 Service properties for Servlet Whiteboard
services.
| Service Property | Type | Description |
|---|---|---|
|
|
optional |
Declares whether the servlet supports the
asynchronous operation mode. Allowed values are |
|
|
optional† |
Register the servlet as an error page for the error
code and/or exception specified; the value may be a fully
qualified exception type name or a three-digit HTTP status code in
the range |
|
|
optional† |
The name of the servlet. This name is used as the
value of the
|
|
|
optional† |
Registration pattern(s) for the servlet. See HTTP_WHITEBOARD_SERVLET_PATTERN. |
|
|
optional |
Enables support for multipart configuration on the
servlet. Allowed values are |
|
|
optional |
The file size threshold after which the file is
stored as a temporary file on disk while uploading. Defaults to
0. Files will be stored in the directory as
specified in |
|
|
optional |
The location where files are stored on disk. Defaults
to the value of |
|
|
optional |
The maximum size for an uploaded file. Defaults to unlimited. Files larger than this size will cause a servlet exception. See HTTP_WHITEBOARD_SERVLET_MULTIPART_MAXFILESIZE. |
|
|
optional |
The maximum size of a
|
servlet.init.* |
optional |
Properties starting with this prefix are provided as
init parameters to the |
† Note that at least one of the following
properties must be specified on Servlet
Whiteboard services:
osgi.http.whiteboard.servlet.pattern
osgi.http.whiteboard.servlet.name
osgi.http.whiteboard.servlet.errorPageServlet objects are initialized by a Http Whiteboard
implementation before they start serving requests. The initialization is
done by calling the Servlet object's
Servlet.init(ServletConfig) method. The
ServletConfig parameter provides access to the initialization
parameters specified when the Servlet object was registered.
Once the servlet is no longer used by the Http Whiteboard implementation
the destroy method is called. Failure during
Servlet.init will prevent the servlet from being used, which
is reflected using a failure DTO. In such a case the system treats the
servlet as unusable and attempts to find an alternative servlet matching
the request.
If the service properties of the servlet Whiteboard service are
modified, the destroy method is called. Subsequently the
servlet is re-initialized. If a Prototype Service Factory is used for the
servlet this re-initialization is done on a new service object.
When multiple Http Whiteboard implementations are present all of
them can potentially process the Servlet. In such situations
it can be useful to associate the servlet with a specific implementation
by specifying the osgi.http.whiteboard.target property on the
Servlet service to match its HttpServiceRuntime
service.
If more than one Http Service Runtime matches the
osgi.http.whiteboard.target property or the property is not
set, the Servlet will be processed by all the matching
implementations. A Servlet service that is processed by more
than one Http Whiteboard implementation will have its init
method called for each implementation that processes this
Servlet. Similarly, the destroy method is called
once when the Servlet is shut down once for each
implementation that processed it. As multiple init and
destroy calls on the same Servlet instance are
generally not desirable, Servlet implementations should be
registered as Prototype Service Factories as defined in the OSGi Core Release 7. This will ensure
that each Http Whiteboard implementation processing the
Servlet will use a separate instance, ensuring that only one
init and destroy call is made per
Servlet object. Servlets not registered as a Prototype
Service Factory may received init and destroy
calls multiple times on the same service object.
The following example code uses Declarative Services annotations to register a servlet whiteboard service.
@HttpWhiteboardServletPattern("/myservlet")
@Component(service = Servlet.class, scope = ServiceScope.PROTOTYPE,
property = "servlet.init.myname=value")
public class MyServlet extends HttpServlet {
private String name = "<not set>";
public void init(ServletConfig config) {
name = config.getInitParameter("myname");
}
protected void doGet(HttpServletRequest req, HttpServletResponse resp)
throws IOException {
resp.setContentType("text/plain");
resp.getWriter().println("Servlet name: " + name);
}
}This example registers the servlet at: /myservlet.
Requests for http://www.acme.com/myservlet map to the
servlet, whose service method is called to process the
request.
To associate the above example servlet with the example
ServletContextHelper in The Servlet Context, add the following
service property:
osgi.http.whiteboard.context.select=(osgi.http.whiteboard.context.name=my-context)This will cause the servlet to move to
http://www.acme.com/myapp/myservlet as configured by the
custom Servlet Context Handler.
Multipart file uploads are supported by specifying the
osgi.http.whiteboard.servlet.multipart.* properties on the
Servlet service registration. The following example illustrates this:
@Component(service = Servlet.class)
@HttpWhiteboardServletPattern("/image")
@HttpWhiteboardServletMultipart(enabled = true, maxFileSize = 200000)
public class ImageServlet extends HttpServlet {
@Override
protected void doPost(HttpServletRequest request,
HttpServletResponse response) throws ServletException, IOException {
Collection<Part> parts = request.getParts();
for (Part part : parts) {
System.out.printf("File %s, %s, %d%n", part.getName(),
part.getContentType(), part.getSize());
try (InputStream is = part.getInputStream()) {
// ...
}
}
}
}Servlets can be used to serve Error Pages. These are invoked when
an exception is thrown during processing or if a servlet uses the
sendError method with a status code between
400 and 599.
For a servlet service to handle error situations the service
property osgi.http.whiteboard.servlet.errorPage must be
set. This property can have multiple values, allowing a single servlet
to handle a variety of error situations. Possible values are 3-digit
HTTP error codes and fully qualified exception names.
Two special error code values are recognized. The special value
4xx means every error code in the 400-499 range. The
special value 5xx means every error code in the 500-599
range. To override such wildcard error page for a specific error,
register an error page with the specific error code and a higher service
ranking. Error pages shadowed by other error pages are reported via the
failure DTOs. A 4xx/5xx wildcard error page is only
reported in the failure DTOs if it is shadowed by another wildcard
page.
Matching exceptions follows the exception hierarchy. First the
most specific exception class - the actual class of the exception - is
looked up. If no matching error page for the most specific exception is
found, the error page for the super class of the exception is looked up
and so on. The process ends by looking up an error page for the
java.lang.Throwable class.
While not being common practice, it is possible to combine the
osgi.http.whiteboard.servlet.errorPage and
osgi.http.whiteboard.servlet.pattern properties. If a
single servlet registration has both these registration properties it is
considered both an ordinary servlet as well as an error page.
If an error or exception occurs for which an error page servlet can be matched, it is invoked to render the error page. If the error page servlet causes an error or exception while handling the request, an implementation built-in error page is returned.
For example:
@Component(service = Servlet.class, scope = ServiceScope.PROTOTYPE)
@HttpWhiteboardServletErrorPage(errorPage = {"java.io.IOException", "500"})
public class MyErrorServlet extends HttpServlet {
...
}The example servlet is invoked in case of a 500 error
code, or if an IOException (or subclass) occurs. If there
is more than one error page registered for the same exception or error
code, service ranking rules are used to select the handling
servlet.
Servlets can use the asynchronous request handling feature, as defined by the servlet specification.
A servlet or servlet filter supporting the asynchronous mode must
declare this with the appropriate service property
osgi.http.whiteboard.servlet.asyncSupported or
osgi.http.whiteboard.filter.asyncSupported.
An example simple asynchronous servlet that handles the servlet requests in a thread from a custom thread pool rather than in the thread provided by the servlet container:
@Component(service = Servlet.class, scope = ServiceScope.PROTOTYPE)
@HttpWhiteboardServletPattern("/as")
@HttpWhiteboardServletAsyncSupported
public class AsyncServlet extends HttpServlet {
ExecutorService executor = Executors.newCachedThreadPool(
r -> new Thread(r, "Pooled Thread"));
protected void doGet(HttpServletRequest req, HttpServletResponse resp)
throws IOException {
doGetAsync(req.startAsync());
}
private void doGetAsync(AsyncContext asyncContext) {
executor.submit(() -> {
try {
PrintWriter writer = asyncContext.getResponse().getWriter();
writer.print("Servlet executed async in: " +
Thread.currentThread()); // writes 'Pooled Thread'
} finally {
asyncContext.complete();
}
return null;
});
}
}Annotations defined in the Servlet API Specifications are ignored by an implementation of the Http Whiteboard Specification. The OSGi service model is used instead by this specification.
Implementations of this specification may support these annotations through a proprietary opt-in mechanism.
Servlet filters provide a mechanism to intercept servlet
invocations. They support modifying the ServletRequest and
ServletResponse objects and are often used to augment web
pages generated by servlets, for example with a common header or footer.
Servlet filters can also be used to handle security, do logging or
transform the content produced by a servlet to a certain format.
Similar to servlets, servlet filters are registered as Whiteboard
services, by registering a javax.servlet.Filter instance in
the Service Registry. The following table describes the supported service
properties. In addition the common properties as described in Table 140.3 on page are supported.
Table 140.5 Service properties for Filter Whiteboard
services.
| Service Property | Type | Description |
|---|---|---|
|
|
optional |
Declares whether the servlet filter supports
asynchronous operation mode. Allowed values are |
|
|
optional |
Select the dispatcher configuration when the servlet
filter should be called. Allowed string values are
|
|
|
optional |
The name of a servlet filter. This name is used as
the value of the |
|
|
optional† |
Apply this servlet filter to the specified URL path patterns. The format of the patterns is specified in the servlet specification. See HTTP_WHITEBOARD_FILTER_PATTERN. |
|
|
optional† |
Apply this servlet filter to the specified URL paths.
The paths are specified as regular expressions following the
syntax defined in the |
|
|
optional† |
Apply this servlet filter to the referenced servlet(s) by name. See HTTP_WHITEBOARD_FILTER_SERVLET. |
filter.init.* |
optional |
Properties starting with this prefix are passed as
init parameters to the |
† Note that at least one of the following
properties must be specified on Filter
Whiteboard services:
osgi.http.whiteboard.filter.pattern
osgi.http.whiteboard.filter.regex
osgi.http.whiteboard.filter.servletSimilar to servlets, Filter objects are initialized by
a Http Whiteboard implementation before they start filtering requests. The
initialization is done by calling the
Filter.init(FilterConfig) method. The
FilterConfig parameter provides access to
filter.init.* properties on the servlet filter service
registration. Once the Filter is no longer used by the Http
Whiteboard implementation, the destroy method is called. When
the service properties on the servlet filter are modified, the
destroy method is called and the servlet filter is
subsequently re-initialized, if it can still be associated with a Http
Whiteboard implementation after the modification. By default, a servlet
filter can be used with any Servlet Context Helper or Http Whiteboard
implementation. To restrict a servlet filter to a single implementation or
a specific Servlet Context Helper, the Common Whiteboard Properties can be used.
To deal with the dynamicity of the Whiteboard service lifecycle, it
is recommended to implement a servlet filter as Prototype Service Factory
service. This will ensure that one single servlet filter instance only
receives one init and one destroy call.
Otherwise a single servlet filter instance can receive multiple such
calls. This is similar to the behavior recommended for Servlet Whiteboard
services.
Multiple servlet filters can process the same servlet
request/response. If more than one Filter matches, the order
in which they are processed is governed by their service ranking. The
servlet filter with the highest ranking is processed first in the filter
chain, while the servlet filter with the lowest ranking is processed last,
before the Servlet.service method is called. In the case of a
service ranking tie, the servlet filter with the lowest
service.id is processed first. After the servlet completes
its service method the filter chain is unwound in reverse
order.
Servlet filters are only applied to servlet requests if they are bound to the same Servlet Context Helper and the same Http Whiteboard implementation.
The example Filter below adds some text before and after the content generated by a servlet:
@Component(scope = ServiceScope.PROTOTYPE)
@HttpWhiteboardFilterPattern("/*")
public class MyFilter implements Filter {
public void init(FilterConfig filterConfig) throws ServletException {}
public void doFilter(ServletRequest request, ServletResponse response,
FilterChain chain) throws IOException, ServletException {
response.getWriter().write("before");
chain.doFilter(request, response);
response.getWriter().write("after");
}
public void destroy() {}
}Servlet Filters are always run after handleSecurity(javax.servlet.http.HttpServletRequest,javax.servlet.http.HttpServletResponse) is called. However in some cases it is necessary
to process servlet requests before security is handled. For example if
all requests must be logged, even ones that are rejected by security. In
other scenarios, requests may need to be prepared for the
handleSecurity call.
A whiteboard Preprocessor service can be registered to handle such cases.
The Preprocessor service only supports the following
service registration properties:
Table 140.6 Service properties for Preprocessor Whiteboard
services.
| Service Property | Type | Description |
|---|---|---|
|
|
optional |
The value of this service property is an LDAP-style
filter expression to select the Http Whiteboard
implementation(s) to handle this Whiteboard service. The LDAP
filter is used to match HttpServiceRuntime services. Each Http Whiteboard
implementation exposes exactly one
|
preprocessor.init.* |
optional |
Properties starting with this prefix are passed as
init parameters to the |
A Preprocessor is invoked before request dispatching
is performed. If multiple pre-processors are registered they are invoked
in the order as described for servlet filters.
The Preprocessor has the same API as the servlet
Filter and is handled in the same way, the
init and destroy are called at the appropriate
life-cycle events. However, as pre-processors are called before
dispatching, the targeted servlet context is not yet know. Therefore the
FilterConfig.getServletContext returns the servlet context
of the backing implementation, the same context as returned by the
request. As a pre-processor instance is not associated with a specific
servlet context, it is safe to implement it as a singleton.
When called in the doFilter method, the pre-processor
can use the FilterChain to invoke the next pre-processor,
or if the end of the chain is reached, start processing the request. The
pre-processor can also terminate the processing and generate a response
directly. Before request processing returns to the pre-processors finishSecurity(javax.servlet.http.HttpServletRequest,javax.servlet.http.HttpServletResponse) is called. If an exception is thrown during
request processing, the exception is propagated through the
pre-processors.
The example Preprocessor below logs a message before
and after request processing:
@Component
public class MyPreprocessor implements Preprocessor {
@Reference(service=LoggerFactory.class)
private Logger logger;
public void init(FilterConfig filterConfig) throws ServletException {}
public void doFilter(ServletRequest request, ServletResponse response,
FilterChain chain) throws IOException, ServletException {
logger.debug("Request processing starts");
chain.doFilter(request, response);
logger.debug("Request processing ends");
}
public void destroy() {}
}A resource is a file containing images, static HTML pages, JavaScript, CSS, sounds, movies, etc. Resources do not require any handling from the bundle. They are transferred directly from their source - usually the JAR file that contains the code for the bundle - to the requester.
Resources can be served by registering a service of any type with a
service registration property that marks it as a resource service:
osgi.http.whiteboard.resource.pattern. The actual service
object registered is not used to serve resources, it is merely used to
inform the Http Whiteboard implementation to serve resources from a
certain source.
The following table describes the supported service properties. In addition the common properties as described in Table 140.3 on page are supported.
Table 140.7 Service properties for resource services.
| Service Property | Type | Description |
|---|---|---|
|
|
required |
The pattern(s) to be used to serve resources. As defined by the [4] Java Servlet 3.1 Specification in section 12.2, Specification of Mappings. This property marks the service as a resource service. |
|
|
required |
The prefix used to map a requested resource to the bundle's entries. If the request's path info is not null, it is appended to this prefix. The resulting string is passed to the getResource(String) method of the associated Servlet Context Helper. |
The examples below use Declarative Services annotations to register a resources service. Note that this service is purely used to convey information to the Http Whiteboard implementation and is never invoked.
@Component(service = MyResourceService.class)
@HttpWhiteboardResource(pattern = "/files/*", prefix = "/www")
public class MyResourceService {}A Http Whiteboard implementation configured on port 80 will serve a
request for http://localhost/files/cheese.html from the
location /www/cheese.html.
The following example maps requests for /favicon.ico to
serve the /logo.png resource. Note that the pattern is not
appended to the prefix as the path info in this case is null.
@Component(service = SomeResourceService.class)
@HttpWhiteboardResource(pattern = "/favicon.ico", prefix = "/logo.png")
public class SomeResourceService {}The above examples use the default ServletContextHelper
implementation, which loads these resources from the bundle that
registered the resource service. For more control around serving
resources, a resources service can be associated to a custom
ServletContextHelper. For example, a custom Servlet Context
Helper can serve resources from locations other than the current
bundle.
Resources and servlets registered with the same Servlet Context
share a single URI namespace. This means that the value specified in
osgi.http.whiteboard.resource.pattern competes with the
osgi.http.whiteboard.servlet.pattern property specified on
servlets. If these values overlap, the rules as outlined in Registering Servlets are used to resolve
conflicts, where resource services are treated just like servlets.
Shadowed resource patterns are reported as FailedResourceDTO.
The servlet specification defines listener interfaces that can be implemented to receive a variety of servlet-related events. When using the Http Whiteboard implementation these listeners can be registered as Whiteboard services.
-
ServletContextListener- Receive notifications when Servlet Contexts are initialized and destroyed. -
ServletContextAttributeListener- Receive notifications for Servlet Context attribute changes. -
ServletRequestListener- Receive notifications for servlet requests coming in and being destroyed. -
ServletRequestAttributeListener- Receive notifications when servlet Request attributes change. -
HttpSessionListener- Receive notifications when Http Sessions are created or destroyed. -
HttpSessionAttributeListener- Receive notifications when Http Session attributes change. -
HttpSessionIdListener- Receive notifications when Http Session ID changes.
Events are sent to listeners registered in the Service Registry with
the osgi.http.whiteboard.listener service property set to
true, independent of case. Listeners can be associated with a
ServletContextHelper as described in Common Whiteboard Properties. Listeners not
specifically associated with a Servlet Context Helper will receive events
relating to the default Servlet Context
Helper.
Multiple listeners of the same type registered with a given Servlet Context Helper are invoked in sequence, service ranking rules are used to determine the order.
Table 140.8 Service properties for listener services.
| Service Property | Type | Description |
|---|---|---|
|
|
required |
When set to |
An example listener that reports on client requests being initialized and destroyed is listed below:
@Component
@HttpWhiteboardListener
public class MyServletRequestListener implements ServletRequestListener {
public void requestInitialized(ServletRequestEvent sre) {
System.out.println("Request initialized for client: " +
sre.getServletRequest().getRemoteAddr());
}
public void requestDestroyed(ServletRequestEvent sre) {
System.out.println("Request destroyed for client: " +
sre.getServletRequest().getRemoteAddr());
}
}For more details on the behavior of the listeners see the [4] Java Servlet 3.1 Specification.
If a Whiteboard service is used by a Http Whiteboard implementation, the following order of actions are performed:
-
The service is obtained from the service registry.
-
For servlets and servlet filters,
initis called.
When the service is not used anymore, these actions are performed:
-
For servlets and servlet filters,
destroyis called. -
The service is released.
Note that some of the above actions may not be performed immediately, allowing an implementation to utilize lazy or asynchronous behavior.
As servlets and servlet filters services might come and go as well
as ServletContextHelper services might come and go, use of
the Whiteboard services can be very dynamic. Therefore servlet and servlet
filter services might transition between bound to a Http Whiteboard
implementation to being unbound and back to be bound. For example, when a
matching Servlet Context Helper with the same name arrives with a higher
ranking than the currently bound Servlet Context Helper, the servlet will
be destroyed and re-initialized, bound to this better matching Servlet
Context Helper. This is to ensure that timing issues cannot dictate the
topology of the system.
As init and destroy are called each time
the service life cycle changes, the recommended way to register services
is to use the Prototype Service scope as defined in the OSGi Core Release 7. This ensures a new
instance is created for each time such service is re-initialized. If the
prototype scope is not used, the service should be prepared that after a
call to destroy a new initialization through
init might follow.
When the Http Whiteboard implementation receives a network request it establishes the processing pipeline based on the available Whiteboard services (servlets, servlet filters and resource services) and executes this pipeline. Between establishing the pipeline and finishing the processing, services used in this pipeline might become unregistered. It is up to the Http Whiteboard implementation whether it completes the active request or throws a Servlet Exception in this case.
The HttpServiceRuntime service represents the runtime state information of a Http Whiteboard implementation. This information is provided through Data Transfer Objects (DTOs). The architecture of OSGi DTOs is described in OSGi Core Release 7.
Each Http Whiteboard implementation registers exactly one
HttpServiceRuntime service which can be used to target
Whiteboard services defined in this specification to a specific Http
Whiteboard implementation.
Implementations of this specification that also implement the Http Service Specification can provide runtime information for servlets
registered using the HttpService via the
HttpServiceRuntime as well. In this case the
osgi.http.service.id service property must be set to
associate the HttpServiceRuntime service with the
HttpService.
The HttpServiceRuntime provides service registration
properties to declare its underlying Http Whiteboard implementation. These
service properties can include implementation-specific key-value pairs.
They also include the following:
Table 140.9 Service properties for the HttpServiceRuntime
service
| Service Property | Type | Description |
|---|---|---|
osgi.http.endpoint |
String+ |
Endpoint(s) where this Http Whiteboard
implementation is listening. Registered Whiteboard services are
made available here. Values could be provided as URLs e.g.
|
osgi.http.service.id |
|
If this Http Whiteboard implementation also
implements the Http Service Specification, this property is
set to hold the See HTTP_SERVICE_ID. |
service.changecount |
Long |
Whenever the DTOs available from the Http Service Runtime service change, the value of this property will increase by an amount of 1 or more. This allows interested
parties to be notified of changes to the DTOs by observing Service
Events of type |
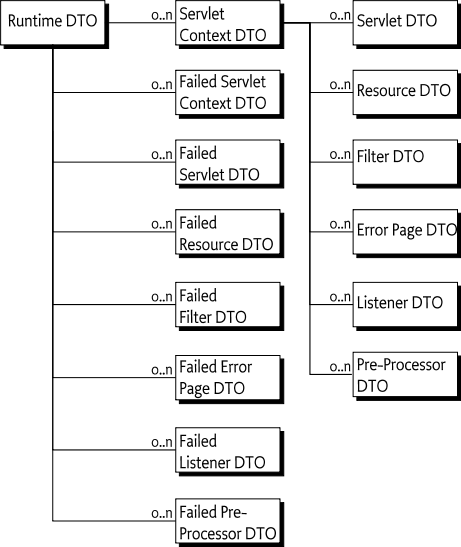
The Http Service Runtime service provides information on registered Whiteboard services through the RuntimeDTO and RequestInfoDTO. The RuntimeDTO provides information on services that have been successfully registered as well as information about the Whiteboard services that were not successfully registered. Whiteboard services that have the required properties set but cannot be processed, are reflected in the failure DTOs. Whiteboard services of interfaces described in this specification that do not have the required properties set are ignored and not reflected in the failure DTOs.
The Runtime DTO can be obtained using the getRuntimeDTO() method. The Runtime DTO provided has the following structure:
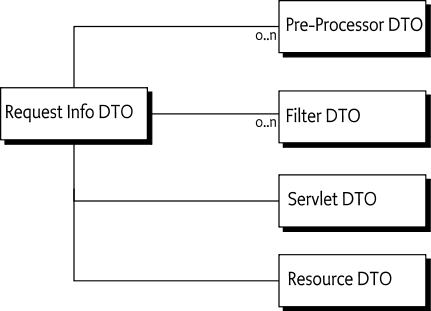
Handlers for a given request path can be found with the calculateRequestInfoDTO(String) method. This method returns a RequestInfoDTO with the following structure:
Where servlets registered via the Http Service Specification are returned via this service, the Servlet DTO will report negative service IDs for these servlets to distinguish them from Servlet Whiteboard services.
Some systems are implemented using a mixture of Http Whiteboard
services and Http Service servlets and contexts as specified in the Http Service Specification. When a servlet is registered with the Http
Service it is either registered with a provided HttpContext
or it uses the default Http Context. It can be desirable to register a
Http Whiteboard filter, listener or error page that also acts on servlets
registered with the Http Service.
A Http Whiteboard service which should be registered with a Http
Context from the Http Service can achieve this by targeting a
ServletContextHelper with the registration property
osgi.http.whiteboard.context.httpservice. The value for this
property is not further specified. Note that this mechanism only works if
the Http Service is provided by the same implementation that also provides
the Http Whiteboard implementation.
The following example registers a servlet filter for all servlets managed by the Http Service.
@Component(service = Filter.class, scope=ServiceScope.PROTOTYPE)
@HttpWhiteboardFilterPattern("/*")
@HttpWhiteboardContextSelect(HttpWhiteboardConstants.HTTP_SERVICE_CONTEXT_FILTER)
public class MyFilter implements FilterThis specification does not provide a way to select in individual Http Context from the Http Service, however a Http Whiteboard implementation may provide an implementation-specific mechanism to do this. Also, the Http Service implementation is not required to register the Http Context objects in the service registry. The matching can be done internally by the implementation.
Association with Http Context from the Http Service can only be done for servlet filters, error pages and listeners. Servlets and resources cannot be associated with Http Contexts managed by the Http Service. If this is attempted this will be reflected in the failure DTOs.
If the Http Whiteboard implementation does not have its port values configured through some other means, the implementation should use the following Framework properties to determine the port values to listen on.
-
org.osgi.service.http.port- This property specifies the port used for servlets and resources accessible via HTTP. The default value for this property is 80. -
org.osgi.service.http.port.secure- This property specifies the port used for servlets and resources accessible via HTTPS. The default value for this property is 443.
The Http Whiteboard implementation bundle must provide the osgi.implementation
capability with name osgi.http. This capability can be used
by provisioning tools and during resolution to ensure that a Http
Whiteboard implementation is present to process the Whiteboard services
defined in this specification. The capability must also declare a uses
constraint for the Servlet and OSGi Http Whiteboard packages and provide
the version of this specification:
Provide-Capability: osgi.implementation;
osgi.implementation="osgi.http";
uses:="javax.servlet, javax.servlet.http,
org.osgi.service.http.context, org.osgi.service.http.whiteboard";
version:Version="1.1"This capability must follow the rules defined for the osgi.implementation Namespace.
Bundles registering services to be picked up by the Http
Whiteboard implementation should require the
osgi.implementation capability. For example:
Require-Capability: osgi.implementation;
filter:="(&(osgi.implementation=osgi.http)
(version>=1.1)(!(version>=2.0)))"
To simplify the creation of this requirement, the RequireHttpWhiteboard annotation can be used.
The Http Whiteboard implementation must provide a capability in
the osgi.contract
namespace with name JavaServlet if it exports the
javax.servlet and javax.servlet.http packages.
See [5] Portable Java Contract Definitions.
Providing the osgi.contract capability enables
developer to build portable bundles for packages that are not versioned
under OSGi Semantic Versioning rules. For more details see osgi.contract Namespace.
If the Servlet API is provided by another bundle, the Http Whiteboard implementation must be a consumer of the API and require the contract.
The bundle providing the HttpServiceRuntime service must provide a capability in the osgi.service
namespace representing this service. This capability must also declare a
uses constraint for the org.osgi.service.http.runtime and
org.osgi.service.http.runtime.dto packages:
Provide-Capability: osgi.service;
objectClass:List<String>="org.osgi.service.http.runtime.HttpServiceRuntime";
uses:="org.osgi.service.http.runtime,org.osgi.service.http.runtime.dto"This capability must follow the rules defined for the osgi.service Namespace.
This section only applies when executing in an OSGi environment which is enforcing Java permissions.
Bundles that need to register Http Whiteboard services must be
granted ServicePermission[interfaceName, REGISTER] where
interface name is the Http Whiteboard service interface name.
The Http Whiteboard implementation must be granted
ServicePermission[interfaceName, GET] to retrieve the Http
Whiteboard services from the service registry.
Bundles that need to introspect the state of the Http runtime will
need
ServicePermission[org.osgi.service.http.runtime.HttpServiceRuntime,
GET] to obtain the HttpServiceRuntime service and access the DTO
types.
The Http Whiteboard implementation must be granted
AdminPermission[*,RESOURCE] so that bundles may use the
default ServletContextHelper implementation. This is
necessary because the implementation of the default
ServletContextHelper must call Bundle.getEntry
to access the resources of a bundle and this method requires the caller
to have AdminPermission[bundle,RESOURCE].
Any bundle may access resources in its own bundle by calling
Class.getResource. This operation is privileged. The
resulting URL object may then be passed to the Http
Whiteboard implementation as the result of a
ServletContextHelper.getResource call. No further
permission checks are performed when accessing bundle entry or resource
URL objects, so the Http Whiteboard implementation does not
need to be granted any additional permissions.
In order to access resources that were not returned from the
default ServletContextHelper implementation, the Http
Whiteboard implementation must be granted sufficient privileges to
access these resources. For example, if the getResource
method of a ServletContextHelper service returns a file
URL, the Http Whiteboard implementation requires the corresponding
FilePermission to read the file. Similarly, if the
getResource method of a ServletContextHelper
service returns an HTTP URL, the Http Whiteboard implementation requires
the corresponding SocketPermission to connect to the
resource.
Therefore, in most cases, the Http Whiteboard implementation
should be a privileged service that is granted sufficient permission to
serve any bundle's resources, no matter where these resources are
located. Therefore, the Http Whiteboard implementation must capture the
AccessControlContext object of the bundle registering a
ServletContextHelper service, and then use the captured
AccessControlContext object when accessing resources
returned by the ServletContextHelper service. This
situation prevents a bundle from supplying resources that it does not
have permission to access.
Therefore, the Http Whiteboard implementation should follow a
scheme like the following example. When using a
ServletContextHelper service, it should capture the
context.
ServiceReference<ServletContextHelper> servletContextHelperReference = ...
AccessControlContext acc = servletContextHelperReference.getBundle()
.adapt(AccessControlContext.class);When a URL returned by the getResource method of a
ServletContextHelper service is used by the Http Whiteboard
implementation, the implementation must use the URL in a
doPrivileged construct using the
AccessControlContext object of the registering
bundle:
AccessController.doPrivileged(
new PrivilegedExceptionAction() {
public Object run() throws Exception {
...
}
}, acc);This ensures the Http Whiteboard implementation can only use the
URL if the bundle registering the ServletContextHelper
service that returned the URL also has permission to use the URL. The
use of a captured AccessControlContext only applies when
accessing URL objects returned by the getResource method of
the ServletContextHelper service.
This specification does not require that the Http Whiteboard
implementation is granted All Permission or wraps calls to the Http
Whiteboard services in a doPrivileged block. Therefore, it
is the responsibility of the Http Whiteboard service implementations to
use a doPrivileged block when performing privileged
operations.
If multipart upload is enabled for a servlet, the uploaded data is usually temporarily written to a file. Therefore if security is enabled file permissions must be granted accordingly.
If a servlet is using the default path to store uploaded data, the
Http Whiteboard implementation needs FilePermission[path,
"read,write,delete"] for that path. As the servlet is reading the
data, the bundle containing the servlet needs FilePermission[path,
"read"] for that path.
If a servlet is providing the path to store uploaded data, the
bundle containing the servlet needs FilePermission[path,
"read,write,delete"] for that path. The Http Whiteboard
implementation needs the same permissions for that path. Therefore, it
is the responsibility of the Http Whiteboard service implementations to
use a doPrivileged block when performing the write
operation.
If security is enabled and any of the above required permissions is not granted, the multipart handling servlet is regarded invalid and will not be registered. This state is reflected in the error DTOs.
Http Whiteboard Context Package Version 1.1.
Bundles wishing to use this package must list the package in the Import-Package header of the bundle's manifest. This package has two types of users: the consumers that use the API in this package and the providers that implement the API in this package.
Example import for consumers using the API in this package:
Import-Package: org.osgi.service.http.context; version="[1.1,2.0)"
Example import for providers implementing the API in this package:
Import-Package: org.osgi.service.http.context; version="[1.1,1.2)"
-
ServletContextHelper- Helper service for a servlet context used by a Http Whiteboard implementation to serve HTTP requests.
Helper service for a servlet context used by a Http Whiteboard implementation to serve HTTP requests.
This service defines methods that the Http Whiteboard implementation may call to get information for a request when dealing with whiteboard services.
Each ServletContextHelper is registered with a
"osgi.http.whiteboard.context.name" service property containing a name to
reference by servlets, servlet filters, resources, and listeners. If there is
more than one ServletContextHelper registered with the same context
name, the one with the highest service ranking is active, the others are
inactive.
A context is registered with the
"osgi.http.whiteboard.context.path" service property to define a path under
which all services registered with this context are reachable. If there is
more than one ServletContextHelper registered with the same path,
each duplicate context path is searched by service ranking order according to
org.osgi.framework.ServiceReference.compareTo(Object) until a
matching servlet or resource is found.
Servlets, servlet filters, resources, and listeners services may be
associated with a ServletContextHelper service with the
"osgi.http.whiteboard.context.select" service property. If the referenced
ServletContextHelper service does not exist or is currently not
active, the whiteboard services for that ServletContextHelper are not
active either.
If no ServletContextHelper service is associated, that is no
"osgi.http.whiteboard.context.select" service property is configured for a
whiteboard service, a default ServletContextHelper is used.
Those whiteboard services that are associated with the same
ServletContextHelper object will share the same
ServletContext object.
The behavior of the methods on the default ServletContextHelper is
defined as follows:
-
getMimeType - Always returns
null. -
handleSecurity - Always returns
true. -
getResource - Assumes the named resource is in the bundle of the whiteboard service, addressed from the root. This method calls the whiteboard service bundle's
Bundle.getEntrymethod, and returns the appropriate URL to access the resource. On a Java runtime environment that supports permissions, the Http Whiteboard implementation needs to be grantedorg.osgi.framework.AdminPermission[*,RESOURCE]. -
getResourcePaths - Assumes that the resources are in the bundle of the whiteboard service. This method calls
Bundle.findEntriesmethod, and returns the found entries. On a Java runtime environment that supports permissions, the Http Whiteboard implementation needs to be grantedorg.osgi.framework.AdminPermission[*,RESOURCE]. -
getRealPath - Always returns
null.
HttpWhiteboardConstants.HTTP_WHITEBOARD_CONTEXT_NAME, HttpWhiteboardConstants.HTTP_WHITEBOARD_CONTEXT_PATH
Thread-safe
HttpServletRequest attribute specifying the scheme used in
authentication. The value of the attribute can be retrieved by
HttpServletRequest.getAuthType.
HttpServletRequest attribute specifying the Authorization
object obtained from the org.osgi.service.useradmin.UserAdmin
service. The value of the attribute can be retrieved by
HttpServletRequest.getAttribute(ServletContextHelper.AUTHORIZATION)
.
HttpServletRequest attribute specifying the name of the
authenticated user. The value of the attribute can be retrieved by
HttpServletRequest.getRemoteUser.
Construct a new context helper.
If needed, the subclass will have to handle the association with a specific bundle.
The bundle to be associated with this context helper.
Construct a new context helper associated with the specified bundle.
The HTTP request.
The HTTP response.
Finishes the security context for the specified request.
Implementations of this service can implement this method to clean up resources which have been setup in handleSecurity(HttpServletRequest, HttpServletResponse).
This method is only called if
handleSecurity(HttpServletRequest, HttpServletResponse) returned
true for the specified request. This method is called once the
pipeline finishes processing or if an exception is thrown from within the
pipeline execution.
The default implementation of this method does nothing.
handleSecurity(HttpServletRequest, HttpServletResponse)
1.1
The name for which to determine the MIME type.
Maps a name to a MIME type.
Called by the Http Whiteboard implementation to determine the MIME type
for the specified name. For whiteboard services, the Http Whiteboard
implementation will call this method to support the
ServletContext method getMimeType. For resource servlets,
the Http Whiteboard implementation will call this method to determine the
MIME type for the Content-Type header in the response.
The MIME type (e.g. text/html) of the specified name or
null to indicate that the Http Whiteboard implementation
should determine the MIME type itself.
The virtual path to be translated to a real path.
Gets the real path corresponding to the given virtual path.
Called by the Http Whiteboard implementation to support the
ServletContext method getRealPath for whiteboard
services.
The real path, or null if the translation cannot be
performed.
The name of the requested resource.
Maps a resource name to a URL.
Called by the Http Whiteboard implementation to map the specified
resource name to a URL. For servlets, the Http Whiteboard implementation
will call this method to support the ServletContext methods
getResource and getResourceAsStream. For resources, the
Http Whiteboard implementation will call this method to locate the named
resource.
The context can control from where resources come. For example, the
resource can be mapped to a file in the bundle's persistent storage area
via BundleContext.getDataFile(name).toURI().toURL() or to a
resource in the context's bundle via getClass().getResource(name)
A URL that a Http Whiteboard implementation can use to read the
resource or null if the resource does not exist.
The partial path used to match the resources, which must start with a /.
Returns a directory-like listing of all the paths to resources within the web application whose longest sub-path matches the supplied path argument.
Called by the Http Whiteboard implementation to support the
ServletContext method getResourcePaths for whiteboard
services.
A Set containing the directory listing, or null if there
are no resources in the web application whose path begins with
the supplied path.
The HTTP request.
The HTTP response.
Handles security for the specified request.
The Http Whiteboard implementation calls this method prior to servicing the specified request. This method controls whether the request is processed in the normal manner or an error is returned.
If the request requires authentication and the Authorization
header in the request is missing or not acceptable, then this method
should set the WWW-Authenticate header in the response object,
set the status in the response object to Unauthorized(401) and return
false. See also RFC
2617: HTTP Authentication: Basic and Digest Access Authentication.
If the request requires a secure connection and the getScheme
method in the request does not return 'https' or some other acceptable
secure protocol, then this method should set the status in the response
object to Forbidden(403) and return false.
When this method returns false, the Http Whiteboard
implementation will send the response back to the client, thereby
completing the request. When this method returns true, the Http
Whiteboard implementation will proceed with servicing the request.
If the specified request has been authenticated, this method must set the
AUTHENTICATION_TYPE request attribute to the type of
authentication used, and the REMOTE_USER request attribute to
the remote user (request attributes are set using the
setAttribute method on the request). If this method does not
perform any authentication, it must not set these attributes.
If the authenticated user is also authorized to access certain resources,
this method must set the AUTHORIZATION request attribute to the
Authorization object obtained from the
org.osgi.service.useradmin.UserAdmin service.
The servlet responsible for servicing the specified request determines
the authentication type and remote user by calling the
getAuthType and getRemoteUser methods, respectively, on
the request.
If there is the need to clean up resources at the end of the request, the
method finishSecurity(HttpServletRequest, HttpServletResponse)
can be implemented. That method is only called if this method returns true.
true if the request should be serviced, false if
the request should not be serviced and Http Whiteboard
implementation will send the response back to the client.
IOException– May be thrown by this method. If this occurs,
the Http Whiteboard implementation will terminate the request
and close the socket.
Http Runtime Package Version 1.1.
Bundles wishing to use this package must list the package in the Import-Package header of the bundle's manifest. This package has two types of users: the consumers that use the API in this package and the providers that implement the API in this package.
Example import for consumers using the API in this package:
Import-Package: org.osgi.service.http.runtime; version="[1.1,2.0)"
Example import for providers implementing the API in this package:
Import-Package: org.osgi.service.http.runtime; version="[1.1,1.2)"
-
HttpServiceRuntime- The HttpServiceRuntime service represents the runtime information of an Http Whiteboard implementation. -
HttpServiceRuntimeConstants- Defines standard names for Http Runtime Service constants.
The HttpServiceRuntime service represents the runtime information of an Http Whiteboard implementation.
It provides access to DTOs representing the current state of the service.
The HttpServiceRuntime service must be registered with the HttpServiceRuntimeConstants.HTTP_SERVICE_ENDPOINT service property.
Thread-safe
Consumers of this API must not implement this type
The request path, relative to the root of the Http Whiteboard implementation.
Return a request info DTO containing the services involved with processing a request for the specified path.
The request info DTO for the specified path.
Defines standard names for Http Runtime Service constants.
Http Runtime Service service property specifying the endpoints upon which the Http Whiteboard implementation is listening.
An endpoint value is a URL or a relative path, to which the Http
Whiteboard implementation is listening. For example,
http://192.168.1.10:8080/ or /myapp/. A relative path may
be used if the scheme and authority parts of the URL are not known, e.g.
in a bridged Http Whiteboard implementation. If the Http Whiteboard
implementation is serving the root context and neither scheme nor
authority is known, the value of the property is "/". Both, a URL and a
relative path, must end with a slash.
An Http Whiteboard implementation can be listening on multiple endpoints.
The value of this service property must be of type String,
String[], or Collection<String>.
Http Runtime Service service property to associate the Http Runtime Service with one or more HttpService services.
If this Http Whiteboard implementation also implements the Http Service
Specification, this service property is set to a collection of
service.id for the HttpService services registered by
this implementation.
The value of this service property must be of type
Collection<Long>.
Http Runtime DTO Package Version 1.1.
Bundles wishing to use this package must list the package in the Import-Package header of the bundle's manifest. This package has two types of users: the consumers that use the API in this package and the providers that implement the API in this package.
Example import for consumers using the API in this package:
Import-Package: org.osgi.service.http.runtime.dto; version="[1.1,2.0)"
Example import for providers implementing the API in this package:
Import-Package: org.osgi.service.http.runtime.dto; version="[1.1,1.2)"
-
BaseServletDTO- Represents common information about ajavax.servlet.Servletservice. -
DTOConstants- Defines standard constants for the DTOs. -
ErrorPageDTO- Represents ajavax.servlet.Servletfor handling errors and currently being used by a servlet context. -
FailedErrorPageDTO- Represents ajavax.servlet.Servletservice registered as an error page but currently not being used by a servlet context due to a problem. -
FailedFilterDTO- Represents a servletFilterservice which is currently not being used by a servlet context due to a problem. -
FailedListenerDTO- Represents a listener service which is currently not being used by a servlet context due to a problem. -
FailedPreprocessorDTO- Represents a preprocessor service which is currently not being used due to a problem. -
FailedResourceDTO- Represents a resource definition which is currently not being used by a servlet context due to a problem. -
FailedServletContextDTO- Represents a servlet context that is currently not used due to some problem. -
FailedServletDTO- Represents ajavax.servlet.Servletservice which is currently not being used by a servlet context due to a problem. -
FilterDTO- Represents a servletjavax.servlet.Filterservice currently being used for by a servlet context. -
ListenerDTO- Represents a listener currently being used by a servlet context. -
PreprocessorDTO- Represents a preprocessororg.osgi.service.http.whiteboard.Preprocessorservice currently being used during request processing. -
RequestInfoDTO- Represents the services used to process a specific request. -
ResourceDTO- Represents a resource definition currently being used by a servlet context. -
RuntimeDTO- Represents the state of a Http Service Runtime. -
ServletContextDTO- Represents ajavax.servlet.ServletContextcreated for servlets, resources, servlet Filters, and listeners associated with that servlet context. -
ServletDTO- Represents ajavax.servlet.Servletcurrently being used by a servlet context.
Represents common information about a javax.servlet.Servlet service.
Not Thread-safe
Specifies whether the servlet supports asynchronous processing.
The servlet initialization parameters as provided during registration of the servlet. Additional parameters like the Http Service Runtime attributes are not included. If the service has no initialization parameters, the map is empty.
The name of the servlet. This value is never null, unless this
object represents a FailedServletDTO or a
FailedErrorPageDTO where the value might be null.
Service property identifying the servlet. In the case of a servlet registered in the service registry and picked up by a Http Whiteboard Implementation, this value is not negative and corresponds to the service id in the registry. If the servlet has not been registered in the service registry, the value is negative and a unique negative value is generated by the Http Service Runtime in this case.
The service id of the servlet context for the servlet represented by this DTO.
The information string from the servlet.
This is the value returned by the Servlet.getServletInfo()
method. For a FailedServletDTO or a FailedErrorPageDTO
this is always null.
Defines standard constants for the DTOs.
An exception occurred during initializing of the service.
This reason can only happen for servlets and servlet filters.
No matching ServletContextHelper.
The service is not registered as a prototype scoped service and is already in use with a servlet context and therefore can't be used with another servlet context.
The service is registered in the service registry but getting the service
fails as it returns null.
Matching ServletContextHelper, but the context is not used due to
a problem with the context.
The servlet is not registered as it is configured to have multipart enabled, but the bundle containing the servlet has no read permission to the default location for the uploaded files.
1.1
The servlet is not registered as it is configured to have multipart enabled, but the bundle containing the servlet has no write permission to the provided location for the uploaded files.
1.1
Service is shadowed by another service.
For example, a service with the same service properties but a higher service ranking.
The service is registered in the service registry but the service properties are invalid.
The servlet is not registered as it is configured to have multipart enabled, but the whiteboard implementation has no write permission to the default location for the uploaded files.
1.1
Represents a javax.servlet.Servlet for handling errors and currently
being used by a servlet context.
Not Thread-safe
The error codes the error page is used for. This array might be empty.
The exceptions the error page is used for. This array might be empty.
Represents a javax.servlet.Servlet service registered as an error
page but currently not being used by a servlet context due to a problem.
As the servlet represented by this DTO is not used due to a failure, the
field FailedErrorPageDTO.servletContextId always returns 0
and does not point to an existing ServletContextHelper.
Not Thread-safe
The reason why the servlet represented by this DTO is not used.
DTOConstants.FAILURE_REASON_UNKNOWN, DTOConstants.FAILURE_REASON_EXCEPTION_ON_INIT, DTOConstants.FAILURE_REASON_NO_SERVLET_CONTEXT_MATCHING, DTOConstants.FAILURE_REASON_SERVICE_NOT_GETTABLE, DTOConstants.FAILURE_REASON_SERVLET_CONTEXT_FAILURE, DTOConstants.FAILURE_REASON_SHADOWED_BY_OTHER_SERVICE
Represents a servlet Filter service which is currently not being used
by a servlet context due to a problem.
As the service represented by this DTO is not used due to a failure, the
field FailedFilterDTO.servletContextId always returns 0 and
does not point to an existing servlet context.
Not Thread-safe
The reason why the servlet filter represented by this DTO is not used.
DTOConstants.FAILURE_REASON_UNKNOWN, DTOConstants.FAILURE_REASON_EXCEPTION_ON_INIT, DTOConstants.FAILURE_REASON_NO_SERVLET_CONTEXT_MATCHING, DTOConstants.FAILURE_REASON_SERVICE_NOT_GETTABLE, DTOConstants.FAILURE_REASON_SERVLET_CONTEXT_FAILURE, DTOConstants.FAILURE_REASON_SHADOWED_BY_OTHER_SERVICE
Represents a listener service which is currently not being used by a servlet context due to a problem.
As the listener represented by this DTO is not used due to a failure, the
field FailedErrorPageDTO.servletContextId always returns 0
and does not point to an existing servlet context.
Not Thread-safe
The reason why the listener represented by this DTO is not used.
DTOConstants.FAILURE_REASON_UNKNOWN, DTOConstants.FAILURE_REASON_EXCEPTION_ON_INIT, DTOConstants.FAILURE_REASON_NO_SERVLET_CONTEXT_MATCHING, DTOConstants.FAILURE_REASON_SERVICE_NOT_GETTABLE, DTOConstants.FAILURE_REASON_SERVLET_CONTEXT_FAILURE, DTOConstants.FAILURE_REASON_SHADOWED_BY_OTHER_SERVICE
Represents a preprocessor service which is currently not being used due to a problem.
1.1
Not Thread-safe
The reason why the preprocessor represented by this DTO is not used.
DTOConstants.FAILURE_REASON_UNKNOWN, DTOConstants.FAILURE_REASON_EXCEPTION_ON_INIT, DTOConstants.FAILURE_REASON_SERVICE_NOT_GETTABLE
Represents a resource definition which is currently not being used by a servlet context due to a problem.
As the resource represented by this DTO is not used due to a failure, the
field FailedResourceDTO.servletContextId always returns 0 and
does not point to an existing servlet context.
Not Thread-safe
The reason why the resource represented by this DTO is not used.
DTOConstants.FAILURE_REASON_UNKNOWN, DTOConstants.FAILURE_REASON_EXCEPTION_ON_INIT, DTOConstants.FAILURE_REASON_NO_SERVLET_CONTEXT_MATCHING, DTOConstants.FAILURE_REASON_SERVICE_NOT_GETTABLE, DTOConstants.FAILURE_REASON_SERVLET_CONTEXT_FAILURE, DTOConstants.FAILURE_REASON_SHADOWED_BY_OTHER_SERVICE
Represents a servlet context that is currently not used due to some problem.
The following fields return an empty array for a
FailedServletContextDTO:
The method ServletContextDTO.attributes returns an empty map for a
FailedServletContextDTO.
Not Thread-safe
The reason why the servlet context represented by this DTO is not used.
DTOConstants.FAILURE_REASON_UNKNOWN, DTOConstants.FAILURE_REASON_EXCEPTION_ON_INIT, DTOConstants.FAILURE_REASON_NO_SERVLET_CONTEXT_MATCHING, DTOConstants.FAILURE_REASON_SERVICE_NOT_GETTABLE, DTOConstants.FAILURE_REASON_SERVLET_CONTEXT_FAILURE, DTOConstants.FAILURE_REASON_SHADOWED_BY_OTHER_SERVICE
Represents a javax.servlet.Servlet service which is currently not
being used by a servlet context due to a problem.
As the servlet represented by this DTO is not used due to a failure, the
field FailedServletDTO.servletContextId always returns 0 and
does not point to an existing servlet context.
Not Thread-safe
The reason why the servlet represented by this DTO is not used.
DTOConstants.FAILURE_REASON_UNKNOWN, DTOConstants.FAILURE_REASON_EXCEPTION_ON_INIT, DTOConstants.FAILURE_REASON_NO_SERVLET_CONTEXT_MATCHING, DTOConstants.FAILURE_REASON_SERVICE_NOT_GETTABLE, DTOConstants.FAILURE_REASON_SERVLET_CONTEXT_FAILURE, DTOConstants.FAILURE_REASON_SHADOWED_BY_OTHER_SERVICE, DTOConstants.FAILURE_REASON_SERVLET_WRITE_TO_LOCATION_DENIED, DTOConstants.FAILURE_REASON_WHITEBOARD_WRITE_TO_DEFAULT_DENIED, DTOConstants.FAILURE_REASON_SERVLET_READ_FROM_DEFAULT_DENIED
Represents a servlet javax.servlet.Filter service currently being
used for by a servlet context.
Not Thread-safe
Specifies whether the servlet filter supports asynchronous processing.
The dispatcher associations for the servlet filter.
The specified names are used to determine in what occasions the servlet
filter is called. This array is never null.
The servlet filter initialization parameters as provided during registration of the servlet filter. Additional parameters like the Http Service Runtime attributes are not included. If the servlet filter has not initialization parameters, this map is empty.
The request mappings for the servlet filter.
The specified patterns are used to determine whether a request is mapped to the servlet filter. This array might be empty.
The request mappings for the servlet filter.
The specified regular expressions are used to determine whether a request is mapped to the servlet filter. This array might be empty.
Service property identifying the servlet filter. In the case of a servlet filter registered in the service registry and picked up by a Http Whiteboard Implementation, this value is not negative and corresponds to the service id in the registry. If the servlet filter has not been registered in the service registry, the value is negative and a unique negative value is generated by the Http Service Runtime in this case.
The service id of the servlet context for the servlet filter represented by this DTO.
The servlet names for the servlet filter.
The specified names are used to determine the servlets whose requests are mapped to the servlet filter. This array might be empty.
Represents a listener currently being used by a servlet context.
Not Thread-safe
Service property identifying the listener. In the case of a Listener registered in the service registry and picked up by a Http Whiteboard Implementation, this value is not negative and corresponds to the service id in the registry. If the listener has not been registered in the service registry, the value is negative and a unique negative value is generated by the Http Service Runtime in this case.
The service id of the servlet context for the listener represented by this DTO.
The fully qualified type names the listener. This array is never empty.
Represents a preprocessor
org.osgi.service.http.whiteboard.Preprocessor service currently being
used during request processing.
1.1
Not Thread-safe
The preprocessor initialization parameters as provided during registration of the preprocessor. Additional parameters like the Http Service Runtime attributes are not included. If the preprocessor has not initialization parameters, this map is empty.
Service property identifying the preprocessor. In the case of a preprocessor registered in the service registry and picked up by a Http Whiteboard Implementation, this value is not negative and corresponds to the service id in the registry. If the preprocessor has not been registered in the service registry, the value is negative and a unique negative value is generated by the Http Service Runtime in this case.
Represents the services used to process a specific request.
Not Thread-safe
The servlet filters processing this request. If no servlet filters are called for processing this request, an empty array is returned.
The resource processing this request. If the request is processed by a
resource, this field points to the DTO of the resource. If the request is
processed by another type of component like a servlet, this field is
null.
The service id of the servlet context processing the request represented by this DTO.
The servlet processing this request. If the request is processed by a
servlet, this field points to the DTO of the servlet. If the request is
processed by another type of component like a resource, this field is
null.
Represents a resource definition currently being used by a servlet context.
Not Thread-safe
The request mappings for the resource.
The specified patterns are used to determine whether a request is mapped
to the resource. This value is never null.
Service property identifying the resource. In the case of a resource registered in the service registry and picked up by a Http Whiteboard Implementation, this value is not negative and corresponds to the service id in the registry. If the resource has not been registered in the service registry, the value is negative and a unique negative value is generated by the Http Service Runtime in this case.
The service id of the servlet context for the resource represented by this DTO.
Represents the state of a Http Service Runtime.
Not Thread-safe
Returns the representations of the error page
javax.servlet.Servlet services associated with this runtime but
currently not used due to some problem. The returned array may be empty.
Returns the representations of the javax.servlet.Filter services
associated with this runtime but currently not used due to some problem.
The returned array may be empty.
Returns the representations of the listeners associated with this runtime but currently not used due to some problem. The returned array may be empty.
Returns the representations of the servlet
org.osgi.service.http.whiteboard.Preprocessor services associated
with this runtime but currently not used due to some problem. The
returned array may be empty.
1.1
Returns the representations of the resources associated with this runtime but currently not used due to some problem. The returned array may be empty.
Returns the representations of the javax.servlet.ServletContext
objects currently not used by the Http service runtime due to some
problem. The returned array may be empty.
Returns the representations of the javax.servlet.Servlet services
associated with this runtime but currently not used due to some problem.
The returned array may be empty.
Returns the representations of the
org.osgi.service.http.whiteboard.Preprocessor objects used by the
Http Service Runtime. The returned array may be empty if the Http Service
Runtime is currently not using any
org.osgi.service.http.whiteboard.Preprocessor objects.
1.1
The DTO for the corresponding
org.osgi.service.http.runtime.HttpServiceRuntime. This value is
never null.
Returns the representations of the javax.servlet.ServletContext
objects used by the Http Service Runtime. The returned array may be empty
if the Http Service Runtime is currently not using any
javax.servlet.ServletContext objects.
Represents a javax.servlet.ServletContext created for servlets,
resources, servlet Filters, and listeners associated with that servlet
context. The Servlet Context is usually backed by a
org.osgi.service.http.context.ServletContextHelper service.
Not Thread-safe
The servlet context attributes.
The value type must be a numerical type, Boolean, String,
DTO or an array of any of the former. Therefore this method will
only return the attributes of the servlet context conforming to this
constraint. Other attributes are omitted. If there are no attributes
conforming to the constraint, an empty map is returned.
The servlet context path.
This is the value returned by the ServletContext.getContextPath()
method.
Returns the representations of the error page Servlet services
associated with this context.
The representations of the error page Servlet services associated
with this context. The returned array may be empty if this context is
currently not associated with any error pages.
Returns the representations of the servlet Filter services
associated with this context.
The representations of the servlet Filter services associated
with this context. The returned array may be empty if this context is
currently not associated with any servlet Filter services.
The servlet context initialization parameters. This is the set of parameters provided when registering this context. Additional parameters like the Http Service Runtime attributes are not included. If the context has no initialization parameters, this map is empty.
Returns the representations of the listener services associated with this context. The representations of the listener services associated with this context. The returned array may be empty if this context is currently not associated with any listener services.
The name of the servlet context. The name of the corresponding org.osgi.service.http.context.ServletContextHelper.
This is the value returned by the
ServletContext.getServletContextName() method.
Returns the representations of the resource services associated with this context. The representations of the resource services associated with this context. The returned array may be empty if this context is currently not associated with any resource services.
Service property identifying the servlet context. In the case of a
servlet context backed by a ServletContextHelper registered in
the service registry and picked up by a Http Whiteboard Implementation,
this value is not negative and corresponds to the service id in the
registry. If the servlet context is not backed by a service registered in
the service registry, the value is negative and a unique negative value
is generated by the Http Service Runtime in this case.
Returns the representations of the Servlet services associated
with this context.
The representations of the Servlet services associated with this
context. The returned array may be empty if this context is currently not
associated with any Servlet services.
Represents a javax.servlet.Servlet currently being used by a servlet
context.
Not Thread-safe
Specifies the size threshold after which the file will be written to
disk. If multipart is not enabled for this servlet, 0 is
returned.
1.1
Specifies the location where the files can be stored on disk. If
multipart is not enabled for this servlet, null is returned.
1.1
Specifies the maximum size of a file being uploaded. If multipart is not
enabled for this servlet, 0 is returned.
1.1
Specifies the maximum request size. If multipart is not enabled for this
servlet, 0 is returned.
1.1
The request mappings for the servlet.
The specified patterns are used to determine whether a request is mapped
to the servlet. This array is never null. It might be empty for
named servlets.
Http Whiteboard Package Version 1.1.
Bundles wishing to use this package must list the package in the Import-Package header of the bundle's manifest. This package has two types of users: the consumers that use the API in this package and the providers that implement the API in this package.
Example import for consumers using the API in this package:
Import-Package: org.osgi.service.http.whiteboard; version="[1.1,2.0)"
Example import for providers implementing the API in this package:
Import-Package: org.osgi.service.http.whiteboard; version="[1.1,1.2)"
-
HttpWhiteboardConstants- Defines standard constants for the Http Whiteboard services. -
Preprocessor- Services registered as aPreprocessorusing a whiteboard pattern are executed for every request before the dispatching is performed.
Defines standard constants for the Http Whiteboard services.
Possible value for the HTTP_WHITEBOARD_FILTER_DISPATCHER property indicating the servlet filter is applied in the asynchronous context.
Java Servlet Specification Version 3.0, Section 6.2.5 Filters and the RequestDispatcher
Possible value for the HTTP_WHITEBOARD_FILTER_DISPATCHER property indicating the servlet filter is applied when an error page is called.
Java Servlet Specification Version 3.0, Section 6.2.5 Filters and the RequestDispatcher
Possible value for the HTTP_WHITEBOARD_FILTER_DISPATCHER property indicating the servlet filter is applied to forward calls to the dispatcher.
Java Servlet Specification Version 3.0, Section 6.2.5 Filters and the RequestDispatcher
Possible value for the HTTP_WHITEBOARD_FILTER_DISPATCHER property indicating the servlet filter is applied to include calls to the dispatcher.
Java Servlet Specification Version 3.0, Section 6.2.5 Filters and the RequestDispatcher
Possible value for the HTTP_WHITEBOARD_FILTER_DISPATCHER property indicating the servlet filter is applied to client requests.
Java Servlet Specification Version 3.0, Section 6.2.5 Filters and the RequestDispatcher
If a servlet filter, error page or listener wants to be registered with the Http Context(s) managed by the Http Service, they can select the contexts having the HTTP_SERVICE_CONTEXT_PROPERTY property using this filter.
1.1
If a servlet filter, error page or listener wants to be registered with the Http Context(s) managed by the Http Service, they can select the contexts having this property.
Servlets or resources registered using this property are treated as an invalid registration.
1.1
Service property prefix referencing a ServletContextHelper service.
For ServletContextHelper services this prefix can be used for service properties to mark them as initialization parameters which can be retrieved from the associated servlet context. The prefix is removed from the service property name to build the initialization parameter name.
For ServletContextHelper services, the value of each
initialization parameter service property must be of type String.
Service property specifying the name of an ServletContextHelper service.
For ServletContextHelper services, this service property must be specified. Context services without this service property are ignored.
Servlet, listener, servlet filter, and resource services might refer to a specific ServletContextHelper service referencing the name with the HTTP_WHITEBOARD_CONTEXT_SELECT property.
For ServletContextHelper services, the value of this service
property must be of type String. The value must follow the
"symbolic-name" specification from Section 1.3.2 of the OSGi Core
Specification.
HTTP_WHITEBOARD_CONTEXT_PATH, HTTP_WHITEBOARD_CONTEXT_SELECT, HTTP_WHITEBOARD_DEFAULT_CONTEXT_NAME
Service property specifying the path of an ServletContextHelper service.
For ServletContextHelper services this service property is required. Context services without this service property are ignored.
This property defines a context path under which all whiteboard services associated with this context are registered. Having different contexts with different paths allows to separate the URL space.
For ServletContextHelper services, the value of this service
property must be of type String. The value is either a slash for
the root or it must start with a slash but not end with a slash. Valid
characters are defined in rfc3986#section-3.3. Contexts with an invalid
path are ignored.
HTTP_WHITEBOARD_CONTEXT_NAME, HTTP_WHITEBOARD_CONTEXT_SELECT
Service property referencing a ServletContextHelper service.
For servlet, listener, servlet filter, or resource services, this service
property refers to the associated ServletContextHelper service.
The value of this property is a filter expression which is matched
against the service registration properties of the
ServletContextHelper service. If this service property is not
specified, the default context is used. If there is no context service
matching, the servlet, listener, servlet filter, or resource service is
ignored.
For example, if a whiteboard service wants to select a servlet context helper with the name "Admin" the expression would be "(osgi.http.whiteboard.context.name=Admin)". Selecting all contexts could be done with "(osgi.http.whiteboard.context.name=*)".
For servlet, listener, servlet filter, or resource services, the value of
this service property must be of type String.
The name of the default ServletContextHelper. If a service is registered with this property, it is overriding the default context with a custom provided context.
Service property specifying whether a servlet Filter service
supports asynchronous processing.
By default servlet filters services do not support asynchronous processing.
The value of this service property must be of type Boolean.
Java Servlet Specification Version 3.0, Section 2.3.3.3 Asynchronous Processing
Service property specifying the dispatcher handling of a servlet
Filter.
By default servlet filter services are associated with client requests only (see value DISPATCHER_REQUEST).
The value of this service property must be of type String,
String[], or Collection<String>. Allowed values are
DISPATCHER_ASYNC, DISPATCHER_ERROR,
DISPATCHER_FORWARD, DISPATCHER_INCLUDE,
DISPATCHER_REQUEST.
Java Servlet Specification Version 3.0, Section 6.2.5 Filters and the RequestDispatcher
Service property prefix referencing a Filter service.
For Filter services this prefix can be used for service properties to mark them as initialization parameters which can be retrieved from the associated filter config. The prefix is removed from the service property name to build the initialization parameter name.
For Filter services, the value of each initialization parameter
service property must be of type String.
Service property specifying the servlet filter name of a Filter
service.
This name is used as the value for the
FilterConfig.getFilterName() method. If this service property is
not specified, the fully qualified name of the service object's class is
used as the servlet filter name.
Servlet filter names should be unique among all servlet filter services associated with a single ServletContextHelper.
The value of this service property must be of type String.
Service property specifying the request mappings for a Filter
service.
The specified patterns are used to determine whether a request should be mapped to the servlet filter. Filter services without this service property or the HTTP_WHITEBOARD_FILTER_SERVLET or the HTTP_WHITEBOARD_FILTER_REGEX service property are ignored.
The value of this service property must be of type String,
String[], or Collection<String>.
Java Servlet Specification Version 3.0, Section 12.2 Specification of Mappings
Service property specifying the request mappings for a servlet
Filter service.
The specified regular expressions are used to determine whether a request
should be mapped to the servlet filter. The regular expressions must
follow the syntax defined in java.util.regex.Pattern. Servlet
filter services without this service property or the
HTTP_WHITEBOARD_FILTER_SERVLET or the
HTTP_WHITEBOARD_FILTER_PATTERN service property are ignored.
The value of this service property must be of type String,
String[], or Collection<String>.
java.util.regex.Pattern
Service property specifying the servlet names for a servlet Filter service.
The specified names are used to determine the servlets whose requests should be mapped to the servlet filter. Servlet filter services without this service property or the HTTP_WHITEBOARD_FILTER_PATTERN or the HTTP_WHITEBOARD_FILTER_REGEX service property are ignored.
The value of this service property must be of type String,
String[], or Collection<String>.
The name of the implementation capability for the Http Whiteboard specification
1.1
Service property to mark a Listener service as a Whiteboard service. Listener services with this property set to the string value "true" will be treated as Whiteboard services opting in to being handled by the Http Whiteboard implementation. If the value "false" is specified, the service is opting out and this case is treated exactly the same as if this property is missing. If an invalid value is specified this is treated as a failure.
The value of this service property must be of type String. Valid
values are "true" and "false" ignoring case.
Service property prefix referencing a Preprocessor service.
For Preprocessor services this prefix can be used for service properties to mark them as initialization parameters which can be retrieved from the associated filter configuration. The prefix is removed from the service property name to build the initialization parameter name.
For Preprocessor services, the value of each initialization
parameter service property must be of type String.
1.1
Service property specifying the request mappings for resources.
The specified patterns are used to determine whether a request should be mapped to resources. Resource services without this service property are ignored.
The value of this service property must be of type String,
String[], or Collection<String>.
Java Servlet Specification Version 3.0, Section 12.2 Specification of Mappings, HTTP_WHITEBOARD_RESOURCE_PREFIX
Service property specifying the resource entry prefix for a resource service.
If a resource service is registered with this property, requests are served with bundle resources.
This prefix is used to map a requested resource to the bundle's entries. The value must not end with slash ("/") with the exception that a name of the form "/" is used to denote the root of the bundle. See the specification text for details on how HTTP requests are mapped.
The value of this service property must be of type String.
Service property specifying whether a Servlet service supports
asynchronous processing.
By default servlet services do not support asynchronous processing.
The value of this service property must be of type Boolean.
Java Servlet Specification Version 3.0, Section 2.3.3.3 Asynchronous Processing
Service property specifying whether a Servlet service acts as an
error page.
The service property values may be the name of a fully qualified exception class, a three digit HTTP status code, the value "4xx" for all error codes in the 400 range, or the value "5xx" for all error codes in the 500 range. Any value that is not a three digit number, or one of the two special values is considered to be the name of a fully qualified exception class.
The value of this service property must be of type String,
String[], or Collection<String>.
Service property prefix referencing a Servlet service.
For Servlet services this prefix can be used for service properties to mark them as initialization parameters which can be retrieved from the associated servlet config. The prefix is removed from the service property name to build the initialization parameter name.
For Servlet services, the value of each initialization parameter
service property must be of type String.
Service property specifying whether a Servlet service has enabled
multipart request processing.
By default servlet services do not have multipart request processing enabled.
The value of this service property must be of type Boolean.
Java Servlet Specification Version 3.0, Section 8.1.5 @MultipartConfig
1.1
Service property specifying the size threshold after which the file will be written to disk.
When not set or when the value is not valid, the default threshold is
determined by the implementation. This property is only evaluated if
HTTP_WHITEBOARD_SERVLET_MULTIPART_ENABLED is set to true
.
The value of this service property must be of type Integer.
Java Servlet Specification Version 3.0, Section 14.4 Deployment Descriptor Diagram
1.1
Service property specifying the location where the files can be stored on disk.
When not set the default location is defined by the value of the system
property "java.io.tmpdir". This property is only evaluated if
HTTP_WHITEBOARD_SERVLET_MULTIPART_ENABLED is set to true
.
The value of this service property must be of type String.
Java Servlet Specification Version 3.0, Section 14.4 Deployment Descriptor Diagram
1.1
Service property specifying the maximum size of a file being uploaded.
When not set or when the value is not valid, the default maximum size is
[@code -1} (no maximum size). This property is only evaluated if
HTTP_WHITEBOARD_SERVLET_MULTIPART_ENABLED is set to true
.
The value of this service property must be of type Long.
Java Servlet Specification Version 3.0, Section 14.4 Deployment Descriptor Diagram
1.1
Service property specifying the maximum request size.
When not set or when the value is not valid, the default maximum request
size is -1 (no maximum size). This property is only evaluated if
HTTP_WHITEBOARD_SERVLET_MULTIPART_ENABLED is set to true
.
The value of this service property must be of type Long.
Java Servlet Specification Version 3.0, Section 14.4 Deployment Descriptor Diagram
1.1
Service property specifying the servlet name of a Servlet
service.
The servlet is registered with this name and the name can be used as a reference to the servlet for filtering or request dispatching.
This name is in addition used as the value for the
ServletConfig.getServletName() method. If this service property
is not specified, the fully qualified name of the service object's class
is used as the servlet name. Filter services may refer to servlets by
this name in their HTTP_WHITEBOARD_FILTER_SERVLET service
property to apply the filter to the servlet.
Servlet names should be unique among all servlet services associated with a single ServletContextHelper.
The value of this service property must be of type String.
Service property specifying the request mappings for a Servlet
service.
The specified patterns are used to determine whether a request should be mapped to the servlet. Servlet services without this service property, HTTP_WHITEBOARD_SERVLET_ERROR_PAGE or HTTP_WHITEBOARD_SERVLET_NAME are ignored.
The value of this service property must be of type String,
String[], or Collection<String>.
Java Servlet Specification Version 3.0, Section 12.2 Specification of Mappings
The version of the implementation capability for the Http Whiteboard specification
1.1
Service property specifying the target filter to select the Http Whiteboard implementation to process the service.
An Http Whiteboard implementation can define any number of service properties which can be referenced by the target filter. The service properties should always include the osgi.http.endpoint service property if the endpoint information is known.
If this service property is not specified, then all Http Whiteboard implementations can process the service.
The value of this service property must be of type String and be
a valid filter string.
Services registered as a Preprocessor using a whiteboard pattern are
executed for every request before the dispatching is performed.
If there are several services of this type, they are run in order of their service ranking, the one with the highest ranking is used first. In the case of a service ranking tie, the service with the lowest service id is processed first.
The preprocessor is handled in the same way as filters. When a preprocessor is put into service Filter.init(javax.servlet.FilterConfig) is called, when it is not used anymore Filter.destroy() is called. As these preprocessors are run before dispatching and therefore the targeted servlet context is not known yet, javax.servlet.FilterConfig.getServletContext() returns the servlet context of the backing implementation. The same context is returned by the request object. The context path is the context path of this underlying servlet context. The passed in chain can be used to invoke the next preprocessor in the chain, or if the end of that chain is reached to start dispatching of the request. A preprocessor might decide to terminate the processing and directly generate a response.
Service properties with the prefix
HttpWhiteboardConstants#HTTP_WHITEBOARD_PREPROCESSOR_INIT_PARAM_PREFIX
are passed as init parameters to this service.
1.1
Thread-safe
Http Whiteboard Annotations Package Version 1.1.
This package contains annotations that can be used to require the Http Whiteboard implementation.
Bundles should not normally need to import this package as the annotations are only used at build-time.
-
RequireHttpWhiteboard- This annotation can be used to require the Http Whiteboard implementation.
This annotation can be used to require the Http Whiteboard implementation. It can be used directly, or as a meta-annotation.
This annotation is applied to several of the Http Whiteboard component property annotations meaning that it does not normally need to be applied to Declarative Services components which use the Http Whiteboard.
CLASS
TYPE, PACKAGE
Http Whiteboard Property Types Package Version 1.1.
When used as annotations, component property types are processed by tools to generate Component Descriptions which are used at runtime.
Bundles wishing to use this package at runtime must list the package in the Import-Package header of the bundle's manifest.
Example import for consumers using the API in this package:
Import-Package: org.osgi.service.http.whiteboard.propertytypes; version="[1.1,2.0)"
-
HttpWhiteboardContext- Component Property Type for theosgi.http.whiteboard.context.nameandosgi.http.whiteboard.context.pathservice properties. -
HttpWhiteboardContextSelect- Component Property Type for theosgi.http.whiteboard.context.selectservice property. -
HttpWhiteboardFilterAsyncSupported- Component Property Type for theosgi.http.whiteboard.filter.asyncSupportedservice property. -
HttpWhiteboardFilterDispatcher- Component Property Type for theosgi.http.whiteboard.filter.dispatcherservice property. -
HttpWhiteboardFilterName- Component Property Type for theosgi.http.whiteboard.filter.nameservice property. -
HttpWhiteboardFilterPattern- Component Property Type for theosgi.http.whiteboard.filter.patternservice property. -
HttpWhiteboardFilterRegex- Component Property Type for theosgi.http.whiteboard.filter.regexservice property. -
HttpWhiteboardFilterServlet- Component Property Type for theosgi.http.whiteboard.filter.servletservice property. -
HttpWhiteboardListener- Component Property Type for theosgi.http.whiteboard.listenerservice property. -
HttpWhiteboardResource- Component Property Type for theosgi.http.whiteboard.resource.patternandosgi.http.whiteboard.resource.prefixservice properties. -
HttpWhiteboardServletAsyncSupported- Component Property Type for theosgi.http.whiteboard.servlet.asyncSupportedservice property. -
HttpWhiteboardServletErrorPage- Component Property Type for theosgi.http.whiteboard.servlet.errorPageservice property. -
HttpWhiteboardServletMultipart- Component Property Type for theosgi.http.whiteboard.servlet.multipart.enabled,osgi.http.whiteboard.servlet.multipart.fileSizeThreshold,osgi.http.whiteboard.servlet.multipart.location,osgi.http.whiteboard.servlet.multipart.maxFileSize, andosgi.http.whiteboard.servlet.multipart.maxRequestSizeservice properties. -
HttpWhiteboardServletName- Component Property Type for theosgi.http.whiteboard.servlet.nameservice property. -
HttpWhiteboardServletPattern- Component Property Type for theosgi.http.whiteboard.servlet.patternservice property. -
HttpWhiteboardTarget- Component Property Type for theosgi.http.whiteboard.targetservice property.
Component Property Type for the osgi.http.whiteboard.context.name and
osgi.http.whiteboard.context.path service properties.
This annotation can be used on a ServletContextHelper to declare the values of the HTTP_WHITEBOARD_CONTEXT_NAME and HTTP_WHITEBOARD_CONTEXT_PATH service properties.
Component Property Types
1.1
CLASS
TYPE
Service property identifying a servlet context helper name.
The context name.
Service property identifying a servlet context helper path.
The context path.
Component Property Type for the osgi.http.whiteboard.context.select
service property.
This annotation can be used on a Http Whiteboard component to declare the value of the HTTP_WHITEBOARD_CONTEXT_SELECT service property.
Component Property Types
1.1
CLASS
TYPE
Service property identifying the select property of a Http Whiteboard component.
The filter expression.
Component Property Type for the
osgi.http.whiteboard.filter.asyncSupported service property.
This annotation can be used on a javax.servlet.Filter to declare the value of the HTTP_WHITEBOARD_FILTER_ASYNC_SUPPORTED service property.
Component Property Types
1.1
CLASS
TYPE
Service property identifying the asynchronous support of a filter.
Whether the filter supports asynchronous processing.
Component Property Type for the
osgi.http.whiteboard.filter.dispatcher service property.
This annotation can be used on a javax.servlet.Filter to declare the value of the HTTP_WHITEBOARD_FILTER_DISPATCHER service property.
Component Property Types
1.1
CLASS
TYPE
Service property identifying dispatcher values for the filter.
The dispatcher values for the filter.
Component Property Type for the osgi.http.whiteboard.filter.name
service property.
This annotation can be used on a javax.servlet.Filter to declare the value of the HTTP_WHITEBOARD_FILTER_NAME service property.
Component Property Types
1.1
CLASS
TYPE
Service property identifying a filter name.
The filter name.
Component Property Type for the osgi.http.whiteboard.filter.pattern
service property.
This annotation can be used on a javax.servlet.Filter to declare the value of the HTTP_WHITEBOARD_FILTER_PATTERN service property.
Component Property Types
1.1
CLASS
TYPE
Service property identifying filter patterns.
The filter patterns.
Component Property Type for the osgi.http.whiteboard.filter.regex
service property.
This annotation can be used on a javax.servlet.Filter to declare the value of the HTTP_WHITEBOARD_FILTER_REGEX service property.
Component Property Types
1.1
CLASS
TYPE
Service property identifying filter regular expressions.
The regular expressions for the filter.
Component Property Type for the osgi.http.whiteboard.filter.servlet
service property.
This annotation can be used on a javax.servlet.Filter to declare the value of the HTTP_WHITEBOARD_FILTER_SERVLET service property.
Component Property Types
1.1
CLASS
TYPE
Service property identifying the servlets for the filter.
The servlet names.
Component Property Type for the osgi.http.whiteboard.listener service
property.
This annotation can be used on a Http Whiteboard listener to declare the
value of the
HTTP_WHITEBOARD_LISTENER service property as being Boolean.TRUE.
Component Property Types
1.1
CLASS
TYPE
Component Property Type for the osgi.http.whiteboard.resource.pattern
and osgi.http.whiteboard.resource.prefix service properties.
This annotation can be used on any service to declare the values of the HTTP_WHITEBOARD_RESOURCE_PATTERN and HTTP_WHITEBOARD_RESOURCE_PREFIX service properties.
Component Property Types
1.1
CLASS
TYPE
Service property identifying resource patterns.
The resource patterns.
Service property identifying resource prefix.
The resource patterns.
Component Property Type for the
osgi.http.whiteboard.servlet.asyncSupported service property.
This annotation can be used on a javax.servlet.Servlet to declare the value of the HTTP_WHITEBOARD_SERVLET_ASYNC_SUPPORTED service property.
Component Property Types
1.1
CLASS
TYPE
Service property identifying the asynchronous support of a servlet.
Whether the servlet supports asynchronous processing.
Component Property Type for the
osgi.http.whiteboard.servlet.errorPage service property.
This annotation can be used on a javax.servlet.Servlet to declare the value of the HTTP_WHITEBOARD_SERVLET_ERROR_PAGE service property.
Component Property Types
1.1
CLASS
TYPE
Service property identifying the error pages of a servlet.
The servlet error pages.
Component Property Type for the
osgi.http.whiteboard.servlet.multipart.enabled,
osgi.http.whiteboard.servlet.multipart.fileSizeThreshold,
osgi.http.whiteboard.servlet.multipart.location,
osgi.http.whiteboard.servlet.multipart.maxFileSize, and
osgi.http.whiteboard.servlet.multipart.maxRequestSize service
properties.
This annotation can be used on a javax.servlet.Servlet to declare the values of the HTTP_WHITEBOARD_SERVLET_MULTIPART_ENABLED, HTTP_WHITEBOARD_SERVLET_MULTIPART_FILESIZETHRESHOLD, HTTP_WHITEBOARD_SERVLET_MULTIPART_LOCATION, HTTP_WHITEBOARD_SERVLET_MULTIPART_MAXFILESIZE, and HTTP_WHITEBOARD_SERVLET_MULTIPART_MAXREQUESTSIZE service properties.
Component Property Types
1.1
CLASS
TYPE
Service property identifying the multipart handling of a servlet.
Whether the servlet supports multipart handling.
Service property identifying the file size threshold for a multipart request handled by a servlet.
The file size threshold for a multipart request..
Service property identifying the location for a multipart request handled by a servlet.
The location for a multipart request..
Service property identifying the max file size for a multipart request handled by a servlet.
The max file size for a multipart request..
Service property identifying the max request size for a multipart request handled by a servlet.
The max request size for a multipart request..
Component Property Type for the osgi.http.whiteboard.servlet.name
service property.
This annotation can be used on a javax.servlet.Servlet to declare the value of the HTTP_WHITEBOARD_SERVLET_NAME service property.
Component Property Types
1.1
CLASS
TYPE
Service property identifying a servlet name.
The servlet name.
Component Property Type for the osgi.http.whiteboard.servlet.pattern
service property.
This annotation can be used on a javax.servlet.Servlet to declare the value of the HTTP_WHITEBOARD_SERVLET_PATTERN service property.
Component Property Types
1.1
CLASS
TYPE
Service property identifying servlet patterns.
The servlet patterns.
Component Property Type for the osgi.http.whiteboard.target service
property.
This annotation can be used on a Http Whiteboard service to declare the value of the HTTP_WHITEBOARD_TARGET service property.
Component Property Types
1.1
CLASS
TYPE
Service property identifying the Http Whiteboard target.
The Http Whiteboard target filter expression.
[1]HTTP 1.0 Specification RFC-1945http://www.ietf.org/rfc/rfc1945.txt, May 1996
[2]HTTP 1.1
Specifications RFCs 7230-7235https://tools.ietf.org/html/rfc7230
https://tools.ietf.org/html/rfc7231
https://tools.ietf.org/html/rfc7232
https://tools.ietf.org/html/rfc7233
https://tools.ietf.org/html/rfc7234
https://tools.ietf.org/html/rfc7235
[3]HTTP/2 Specificationshttps://http2.github.io
[4]Java Servlet 3.1 Specificationhttps://jcp.org/aboutJava/communityprocess/final/jsr340/
[5]Portable Java Contract Definitionshttps://docs.osgi.org/reference/portable-java-contracts.html
[6]RFC 2617: HTTP Authentication: Basic and Digest Access Authenticationhttp://www.ietf.org/rfc/rfc2617.txt
[7]Whiteboard Patternhttps://docs.osgi.org/whitepaper/whiteboard-pattern/
-
Added finishSecurity(javax.servlet.http.HttpServletRequest,javax.servlet.http.HttpServletResponse) to the Servlet Context Helper.
-
Added Servlet support for Multipart Configuration Handling. See Table 140.4.
-
Added Servlet Pre-Processors.
-
Added
service.changecountservice property to Http Service Runtime Service. See Table 140.9 -
Added component property types and annotations, see org.osgi.service.http.whiteboard.propertytypes in the API section.
-
Added the RequireHttpWhiteboard annotation.